New claim staked for metallic hydrogen
A team of scientists may have given hydrogen a squeeze strong enough to turn it into a metal. But critics vigorously dispute the claim.
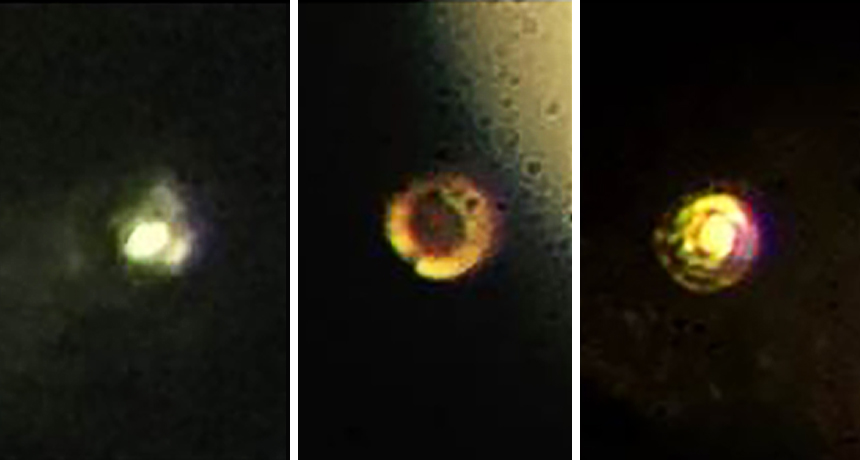
Researchers from Harvard University report that under extremely high pressures hydrogen became reflective — one of the key properties of a metal. The feat required compressing hydrogen to 4.9 million times atmospheric pressure, the scientists report online January 26 in Science.
If correct, the result would be the culmination of a decades-long search for a material that could have unusual properties such as superconductivity — the ability to conduct electricity without resistance.
But physicist Eugene Gregoryanz of the University of Edinburgh, who works on similar experiments, decries the study’s publication as a failure of the journal’s review process. Given the evidence presented in the paper, Gregoryanz is skeptical that the claimed pressures were actually reached and notes that the researchers presented results from only one experiment. “How is it possible to do only one experiment and claim such a big thing?” he says.
Physicist Alexander Goncharov of the Carnegie Institution for Science in Washington, D.C., also takes issue with the researchers’ conclusions. “It’s not shown whether they have hydrogen at all at high pressure,” Goncharov says.
Not everyone is so skeptical. “I think there’s a good chance that it’s correct,” says theoretical physicist David Ceperley of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. The pressure at which the hydrogen became reflective is about where theoretical physicists have calculated that a metal should form, Ceperley says.
Theorists’ calculations also indicate that metallic hydrogen could be a high-temperature superconductor (SN: 8/20/16, p. 18). Most superconductors work only in extreme cold, but metallic hydrogen might function even at room temperature — higher than any other known superconductor. If so, its discovery would raise hopes that superconducting metallic hydrogen could be used in power lines, making transmission of electricity vastly more efficient.
To put the pressure on hydrogen, scientists capture it as a gas between the tips of two diamonds and squeeze them together. It’s no easy task. “The problem in making metallic hydrogen has been that the predicted pressures have been very high,” says physicist Isaac Silvera of Harvard University, a coauthor of the study. “Diamonds always break before you can obtain those pressures.”
To stave off breakage, the scientists smoothed the surface of the diamonds to remove any defects and covered the gems in a thin layer of aluminum oxide to prevent hydrogen from diffusing inside and creating cracks. The researchers also cooled the setup to temperatures of 83 kelvins (−190° Celsius) or below. As the scientists ratcheted up the pressure, the hydrogen first turned black, indicating a possible semiconducting phase, then became reflective, indicating a metal. The metallic hydrogen could be either a solid or a liquid, Silvera says.
But such experiments are tricky — only a few teams of researchers in the world are capable of performing them. One of the pitfalls can be that the hydrogen escapes from the chamber without the scientists realizing it. However, Silvera says, “We’re sure we have hydrogen in there.”
Some previous metallic hydrogen experiments have monitored hydrogen as the pressure is ramped up to help ensure that the hydrogen hasn’t escaped and to study its evolution. To do so, scientists use a technique called Raman spectroscopy, which involves shining a laser through the diamonds and observing the scattered light. But at pressures this high, lasers could cause the diamonds to break, Silvera says. So the researchers used lasers only after the sample had reached the metallic state.
Silvera’s group is not the first to announce the discovery of metallic hydrogen. Earlier claims of finding the metal have been overturned (SN: 12/17/11, p. 9). “It’s not the last word,” says Ceperley. “It should encourage all the other groups to come out and try to reproduce it.”